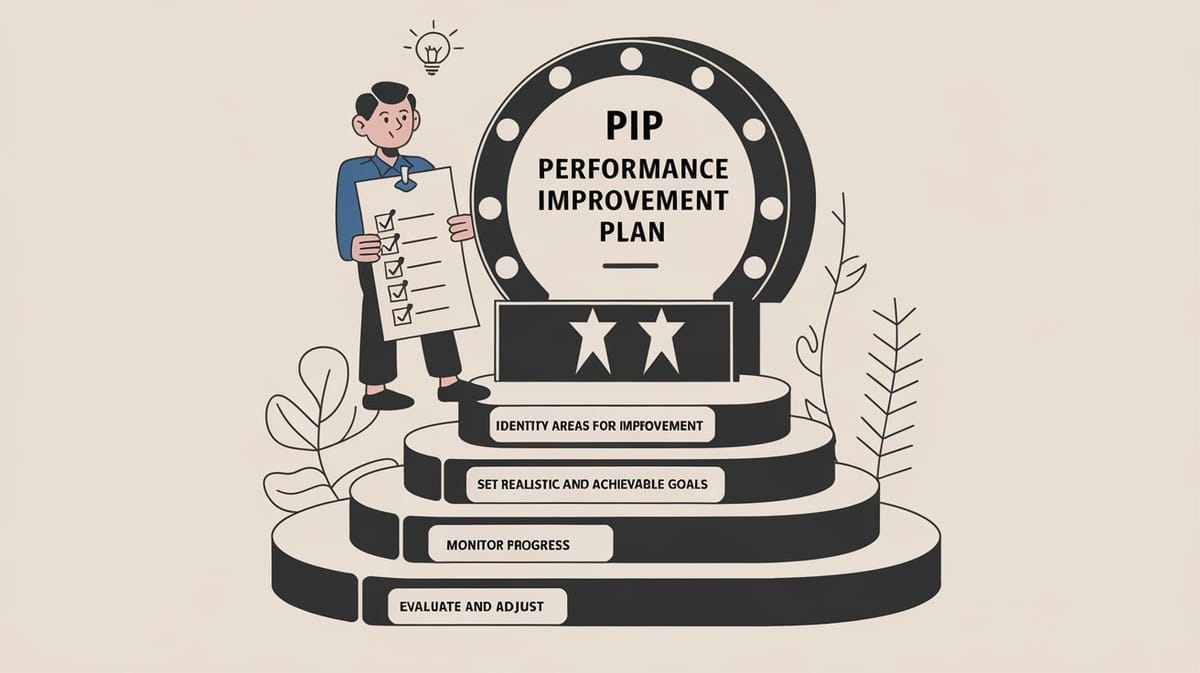
Guide to Performance Improvement Plan (AKA PIP) in the workplace
In today's dynamic and competitive business environment, organizations are increasingly focusing on enhancing employee performance to achieve strategic goals. A Performance Improvement Plan (PIP) is a structured tool used by employers to address and improve an employee's work performance. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of PIPs, their significance, and how they can be effectively implemented to foster a culture of continuous improvement and accountability.
A PIP is typically initiated when an employee's performance falls below the expected standards, and it serves as a formal agreement between the employer and the employee to address specific areas of concern. The primary objective of a PIP is not punitive but rather developmental, offering employees a clear path to meet performance expectations through targeted support and resources.
Implementing a PIP involves several critical steps, including identifying performance gaps, setting achievable goals, and providing regular feedback. It is essential for managers to approach PIPs with transparency and empathy, ensuring that employees understand the expectations and have the necessary tools to succeed.
Moreover, a well-executed PIP can lead to significant benefits for both the employee and the organization. It can enhance employee engagement, reduce turnover, and ultimately contribute to a more productive and motivated workforce. However, it is crucial to handle PIPs with care to avoid potential legal implications and to maintain a positive workplace culture.
You can also visit Oncely.com to find more Top Trending AI Tools. Oncely partners with software developers and companies to present exclusive deals on their products. One unique aspect of Oncely is its “Lifetime Access” feature, where customers can purchase a product once and gain ongoing access to it without any recurring fees. Oncely also provides a 60-day money-back guarantee on most purchases, allowing customers to try out the products and services risk-free.
Oncely are hunting for the most fantastic AI & Software lifetime deals like the ones below or their alternatives:

Table of Contents
- Understanding Performance Improvement Plans
- Purpose and Importance of Performance Improvement Plans
- Key Components of a Performance Improvement Plan
- Legal and Ethical Considerations
- Best Practices for Implementing Performance Improvement Plans
- Challenges and Considerations in Using PIPs
- Steps to Implement a Performance Improvement Plan
- Identifying Performance Issues
- Developing Measurable Objectives
- Creating a Detailed Plan
- Engaging in Open Communication
- Monitoring Progress and Providing Feedback
- Best Practices in Performance Improvement Plans
- Clear Communication and Documentation
- Setting Realistic and Measurable Goals
- Regular Feedback and Support
- Common Challenges in Performance Improvement Plans
- Resistance to Change
- Inadequate Training and Resources
- Inconsistent Implementation
- Lack of Follow-Up
- Legal and Ethical Considerations
Understanding Performance Improvement Plans
Purpose and Importance of Performance Improvement Plans
Performance Improvement Plans (PIPs) are structured tools used by organizations to address and improve employee performance issues. They serve as a formal mechanism to help employees meet specific job performance standards and expectations. PIPs are crucial in maintaining workplace productivity and ensuring that employees have the opportunity to succeed in their roles. According to a study by the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM), approximately 77% of organizations use PIPs as part of their performance management strategy.
The primary purpose of a PIP is to provide a clear framework for employees to improve their performance. It outlines specific areas where performance is lacking, sets measurable goals, and provides a timeline for achieving these goals. This structured approach not only helps employees understand what is expected of them but also provides managers with a consistent method for addressing performance issues.
Key Components of a Performance Improvement Plan
A well-structured PIP typically includes several key components that ensure clarity and effectiveness. These components are designed to provide a comprehensive approach to performance improvement:
-
Performance Issues: Clearly identify and document the specific performance issues that need to be addressed. This includes providing examples and evidence of the performance gaps. For instance, if an employee is not meeting sales targets, the PIP should include data on their current performance compared to the expected targets.
-
Goals and Objectives: Set clear, achievable goals that the employee needs to meet within a specified timeframe. These goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For example, an employee might be required to increase their sales by 20% over the next three months.
-
Action Plan: Outline the steps the employee will take to improve their performance. This may include additional training, mentorship, or changes in work processes. The action plan should be detailed and provide a roadmap for the employee to follow.
-
Support and Resources: Identify the support and resources available to the employee to help them succeed. This could include access to training programs, regular feedback sessions with a manager, or the assignment of a mentor.
-
Evaluation and Review: Establish a process for evaluating the employee's progress and providing feedback. This includes setting regular check-ins to discuss progress and make any necessary adjustments to the PIP. The evaluation process should be transparent and objective, ensuring that the employee understands how their performance is being assessed.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Implementing a PIP involves several legal and ethical considerations that organizations must be aware of to avoid potential pitfalls. It is essential to ensure that PIPs are applied consistently and fairly across all employees to prevent claims of discrimination or unfair treatment. According to the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC), employers must ensure that PIPs do not disproportionately affect employees based on race, gender, age, or other protected characteristics.
Additionally, PIPs should be documented thoroughly to provide a clear record of the performance issues, the steps taken to address them, and the outcomes. This documentation can be crucial in defending against any legal claims that may arise from the PIP process.
Best Practices for Implementing Performance Improvement Plans
To maximize the effectiveness of PIPs, organizations should follow best practices that align with their performance management strategies. These practices include:
-
Clear Communication: Ensure that the PIP is communicated clearly to the employee, with an emphasis on the intent to support their improvement. Managers should discuss the PIP in a private setting and provide an opportunity for the employee to ask questions and provide input.
-
Consistent Application: Apply PIPs consistently across the organization to ensure fairness and avoid perceptions of bias. This includes using the same criteria and processes for all employees who are placed on a PIP.
-
Regular Monitoring: Monitor the employee's progress regularly and provide constructive feedback. This helps keep the employee motivated and allows for timely adjustments to the PIP if necessary.
-
Positive Reinforcement: Recognize and reward improvements in performance to encourage continued progress. Positive reinforcement can be a powerful motivator and can help build the employee's confidence.
Challenges and Considerations in Using PIPs
While PIPs can be effective tools for improving performance, they also present certain challenges and considerations. One of the main challenges is the potential for PIPs to be perceived as punitive rather than supportive. To mitigate this, organizations should emphasize the developmental aspect of PIPs and ensure that they are used as a tool for growth rather than punishment.
Another consideration is the potential impact on employee morale. Employees placed on a PIP may feel demotivated or anxious about their job security. It is important for managers to provide reassurance and support throughout the process to help alleviate these concerns.
Finally, organizations must be prepared to take further action if the PIP does not result in the desired improvement. This may include reassigning the employee to a different role, providing additional training, or, in some cases, termination of employment. It is crucial to handle these situations with sensitivity and in accordance with company policies and legal requirements.
In conclusion, Performance Improvement Plans are valuable tools for addressing performance issues and supporting employee development. By understanding their purpose, components, and best practices, organizations can effectively implement PIPs to enhance workplace productivity and employee success.
Steps to Implement a Performance Improvement Plan
Identifying Performance Issues
The initial step in implementing a Performance Improvement Plan (PIP) is to accurately identify the performance issues that need addressing. This involves a thorough assessment of the employee's current performance against the expected standards. Performance issues can range from not meeting specific job-related goals to exhibiting unprofessional behavior in the workplace. It is crucial to document these issues clearly and objectively to ensure that the PIP is based on factual evidence rather than subjective opinions. According to Venngage, pinpointing the problem is the first step in crafting an effective PIP.
Developing Measurable Objectives
Once the performance issues have been identified, the next step is to develop measurable objectives that the employee needs to achieve. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). The use of SMART goals ensures that the employee has a clear understanding of what is expected and can track their progress over time. As noted by BetterUp, goals should be explicit and measurable to provide a clear path for improvement. This step is critical as it lays the foundation for the entire PIP process, providing both the employee and the employer with a clear roadmap to follow.
Creating a Detailed Plan
With the objectives in place, the next step is to create a detailed plan that outlines the actions the employee will take to meet these objectives. This plan should include specific tasks, deadlines, and any resources or support the employee will need. It is also important to consider any training or development opportunities that could help the employee improve their performance. According to Forbes, the plan should be discussed with the company's HR department to ensure it aligns with organizational policies and practices. The HR department can also provide templates and guidance to streamline the process.
Engaging in Open Communication
Effective communication is a key component of a successful PIP. Once the plan is drafted, it should be discussed with the employee in a formal meeting. This meeting should be an open dialogue where the employee is encouraged to ask questions and provide feedback. The goal is to ensure that the employee fully understands the plan, the expectations, and the consequences of not meeting the objectives. As highlighted by SHRM, the PIP should signal a commitment to helping the employee improve, rather than being a precursor to termination. This mutual understanding is crucial for the plan's success.
Monitoring Progress and Providing Feedback
The final step in implementing a PIP is to monitor the employee's progress and provide regular feedback. This involves setting up regular check-ins to discuss the employee's progress towards meeting the objectives. Constructive feedback should be provided during these meetings to help the employee stay on track and make any necessary adjustments to their approach. According to Venngage, incorporating feedback mechanisms is essential for the success of a PIP. These mechanisms can include feedback from team members, superiors, or even self-assessment. The goal is to provide the employee with the support they need to succeed and to make any necessary adjustments to the plan as needed.
In summary, implementing a Performance Improvement Plan involves a systematic approach that includes identifying performance issues, developing measurable objectives, creating a detailed plan, engaging in open communication, and monitoring progress. By following these steps, organizations can effectively address performance deficiencies and help employees reach their full potential.
Best Practices in Performance Improvement Plans
Clear Communication and Documentation
Effective communication is a cornerstone of successful Performance Improvement Plans (PIPs). It is essential to ensure that all parties involved understand the objectives, expectations, and timelines associated with the PIP. Clear communication helps in setting realistic goals and reduces misunderstandings. According to a study by the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM), organizations that prioritize clear communication in PIPs see a 30% improvement in employee performance outcomes (SHRM).
Documentation is equally important. Every step of the PIP process should be documented meticulously. This includes initial performance assessments, meetings, feedback sessions, and progress evaluations. Proper documentation not only provides a clear record of the process but also serves as a legal safeguard for the organization. It ensures that the PIP is conducted fairly and transparently, which is crucial in maintaining trust and accountability.
Setting Realistic and Measurable Goals
One of the best practices in implementing PIPs is setting realistic and measurable goals. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). This approach ensures that employees have a clear understanding of what is expected of them and can track their progress effectively. Research indicates that employees are 50% more likely to improve their performance when goals are clearly defined and measurable (Harvard Business Review).
Moreover, involving employees in the goal-setting process can enhance their commitment to the PIP. When employees have a say in setting their objectives, they are more likely to take ownership of their performance improvement journey. This participatory approach fosters a sense of responsibility and motivation, which are critical for the success of the PIP.
Regular Feedback and Support
Providing regular feedback and support is crucial in the PIP process. Feedback should be constructive, focusing on specific behaviors and outcomes rather than personal attributes. Regular feedback sessions allow employees to understand their progress and make necessary adjustments to their performance strategies. According to a Gallup study, employees who receive regular feedback are 3.6 times more likely to be engaged in their work (Gallup).
Support from managers and HR professionals is also vital. This support can take various forms, such as additional training, mentoring, or resources needed to achieve the set goals. By providing the necessary support, organizations demonstrate their commitment to employee development, which can significantly enhance the effectiveness of PIPs.
Common Challenges in Performance Improvement Plans
Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a common challenge in implementing PIPs. Employees may perceive PIPs as punitive rather than developmental, leading to resistance and disengagement. This resistance can stem from fear of failure, lack of trust in management, or previous negative experiences with PIPs. To overcome this challenge, it is essential to frame PIPs as opportunities for growth and development rather than as disciplinary measures. Open communication and transparency can help in alleviating fears and building trust.
Inadequate Training and Resources
Another significant challenge is the lack of adequate training and resources. Employees may struggle to meet PIP objectives if they do not have access to the necessary tools, training, or support. This can lead to frustration and decreased morale. Organizations should ensure that employees have access to the resources they need to succeed. This includes providing relevant training programs, access to technology, and support from supervisors and peers.
Inconsistent Implementation
Inconsistent implementation of PIPs can undermine their effectiveness. This inconsistency can arise from a lack of standardized procedures or varying levels of commitment from managers. To address this challenge, organizations should establish clear guidelines and procedures for implementing PIPs. Training managers on these procedures can ensure consistency and fairness in the PIP process. A study by the Human Capital Institute found that organizations with standardized PIP processes are 40% more likely to achieve desired performance outcomes (Human Capital Institute).
Lack of Follow-Up
A lack of follow-up is another common challenge in PIPs. Without regular follow-up, it is difficult to assess progress and make necessary adjustments to the PIP. This can lead to stagnation and failure to achieve desired outcomes. Regular follow-up meetings should be scheduled to review progress, provide feedback, and make any necessary changes to the PIP. This ongoing engagement helps keep employees motivated and focused on their performance goals.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Legal and ethical considerations can also pose challenges in the PIP process. Organizations must ensure that PIPs are implemented fairly and without discrimination. This includes providing equal opportunities for all employees to improve their performance and ensuring that PIPs do not disproportionately affect certain groups. Failure to adhere to legal and ethical standards can result in legal challenges and damage to the organization's reputation. It is crucial for HR professionals to stay informed about relevant laws and regulations and to ensure that PIPs are conducted in compliance with these standards.
In summary, while PIPs can be effective tools for improving employee performance, they require careful planning and execution. By adhering to best practices and addressing common challenges, organizations can enhance the effectiveness of PIPs and foster a culture of continuous improvement and development.